
Amid the global debate about race relations, colonialism and slavery, some of the Europeans and Americans who made their fortunes in trading human beings have seen their legacies reassessed, their statues toppled and their names removed from public buildings.
Nigerian journalist and novelist Adaobi Tricia Nwaubani writes that one of her ancestors sold slaves, but argues that he should not be judged by today’s standards or values.

My great-grandfather, Nwaubani Ogogo Oriaku, was what I prefer to call a businessman, from the Igbo ethnic group of south-eastern Nigeria. He dealt in a number of goods, including tobacco and palm produce. He also sold human beings.
“He had agents who captured slaves from different places and brought them to him,” my father told me.
Nwaubani Ogogo’s slaves were sold through the ports of Calabar and Bonny in the south of what is today known as Nigeria.
People from ethnic groups along the coast, such as the Efik and Ijaw, usually acted as stevedores for the white merchants and as middlemen for Igbo traders like my great-grandfather.
They loaded and offloaded ships and supplied the foreigners with food and other provisions. They negotiated prices for slaves from the hinterlands, then collected royalties from both the sellers and buyers.
 Several European nations had slave compounds in what is now Nigeria. Image copyright GETTY IMAGES
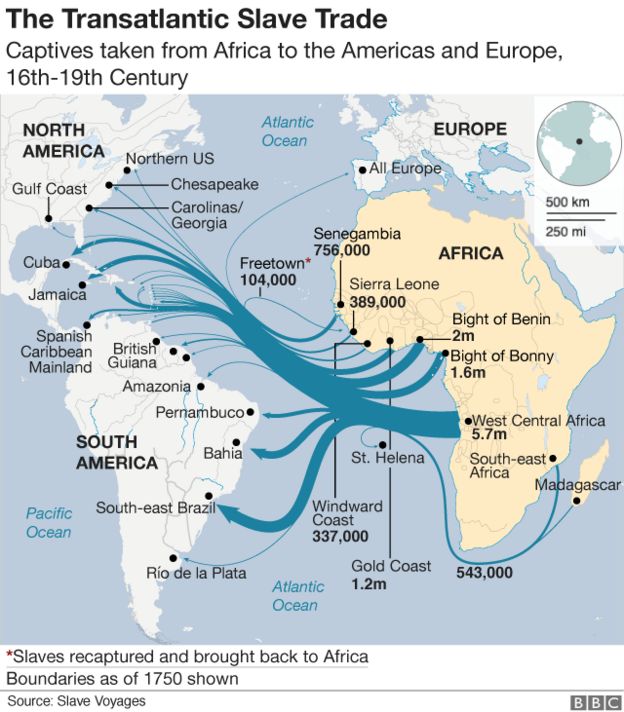
Several European nations had slave compounds in what is now Nigeria. Image copyright GETTY IMAGESAbout 1.5 million Igbo slaves were shipped across the Atlantic Ocean between the 15th and 19th Centuries.
More than 1.5 million Africans were shipped to what was then called the New World – the Americas – through the Calabar port, in the Bight of Bonny, making it one of the largest points of exit during the transatlantic trade.


The only life they knew
Nwaubani Ogogo lived in a time when the fittest survived and the bravest excelled. The concept of “all men are created equal” was completely alien to traditional religion and law in his society.
Assessing the people of Africa’s past by today’s standards would compel us to cast the majority of our heroes as villains”
It would be unfair to judge a 19th Century man by 21st Century principles.
Assessing the people of Africa’s past by today’s standards would compel us to cast the majority of our heroes as villains, denying us the right to fully celebrate anyone who was not influenced by Western ideology.
Igbo slave traders like my great-grandfather did not suffer any crisis of social acceptance or legality. They did not need any religious or scientific justifications for their actions. They were simply living the life into which they were raised.
That was all they knew.

Slaves buried alive
The most popular story I’ve heard about my great-grandfather was how he successfully confronted officials of the British colonial government after they seized some of his slaves.
My great-grandfather apparently did not consider it fair that his slaves had been seized”
The slaves were being transported by middlemen, along with a consignment of tobacco and palm produce, from Nwaubani Ogogo’s hometown of Umuahia to the coast.
My great-grandfather apparently did not consider it fair that his slaves had been seized.
Buying and selling of human beings among the Igbo had been going on long before the Europeans arrived. People became slaves as punishment for crime, payment for debts, or prisoners of war.
The successful sale of adults was considered an exploit for which a man was hailed by praise singers, akin to exploits in wrestling, war, or in hunting animals like the lion.
Igbo slaves served as domestic servants and labourers. They were sometimes also sacrificed in religious ceremonies and buried alive with their masters to attend to them in the next world.
Slavery was so ingrained in the culture that a number of popular Igbo proverbs make reference to it:
- Anyone who has no slave is his own slave
- A slave who looks on while a fellow slave is tied up and thrown into the grave with his master should realise that the same thing could be done to him someday
- It is when the son is being given advice that the slave learns
The arrival of European merchants offering guns, mirrors, gin, and other exotic goods in exchange for humans massively increased demand, leading people to kidnap others and sell them.

How slaves were traded in Africa
 Image copyrightGETTY IMAGES
Image copyrightGETTY IMAGES- European buyers tended to remain on the coast
- African sellers brought slaves from the interior on foot
- Journeys could be as long as 485km (300 miles)
- Two captives were typically chained together at the ankle
- Columns of captives were tied together by ropes around their necks
- 10%-15% of captives died on the way
Source: Encyclopaedia Britannica


Resisting abolition
The trade in African people continued until 1888, when Brazil became the last country in the Western hemisphere to abolish it.
We think this trade must go on.That is the verdict of our oracle and our priests”

When the British extended their rule to south-eastern Nigeria in the late 19th Century and early 20th Century, they began to enforce abolition through military action.
But by using force rather than persuasion, many local people such as my great-grandfather may not have understood that abolition was about the dignity of humankind and not a mere change in economic policy that affected demand and supply.
“We think this trade must go on,” one local king in Bonny infamously said in the 19th Century.
“That is the verdict of our oracle and our priests. They say that your country, however great, can never stop a trade ordained by God.”
 Image copyrightGETTY IMAGES
Image copyrightGETTY IMAGESAs far as my great-grandfather was concerned, he had a bona fide trading licence from the Royal Niger Company, a British company that administered commerce in the region in the last quarter of the 19th Century.
So when his property was seized, an aggrieved Nwaubani Ogogo boldly went to see the colonial officers responsible and presented them with his licence. They released his goods, and his slaves.
“The white people apologised to him,” my father said.
 Image copyrightADAOBI TRICIA NWAUBANI
Image copyrightADAOBI TRICIA NWAUBANI
Slave trade in the 20th Century
Acclaimed Igbo historian Adiele Afigbo described the slave trade in south-eastern Nigeria which lasted until the late 1940s and early 1950s as one of the best kept secrets of the British colonial administration.
While the international trade ended, the local trade continued.
“The government was aware of the fact that the coastal chiefs and the major coastal traders had continued to buy slaves from the interior,” wrote Afigbo in The Abolition of the Slave Trade in Southern Nigeria: 1885 to 1950.
He added that the British tolerated the ongoing trade on political and economic grounds.
 Image copyrightGETTY IMAGES
Image copyrightGETTY IMAGESThey needed the slave-trading chiefs for effective local governance, and for the expansion and growth of legitimate trade.
Sometimes, they also turned a blind eye rather than jeopardise a useful alliance, as seems to have been the case when they returned Nwaubani Ogogo’s slaves.
That incident deified Nwaubani Ogogo among his people. Here was a man who successfully confronted the white powers from overseas. I have heard the story from relatives, and have read about it.
It was also the beginning of a relationship of mutual respect with the colonialists that led to Nwaubani Ogogo being appointed a paramount chief by the British administration.
He was the government’s representative to the people in his region, in a system known as indirect rule.
- 1833 Parliament outlawed slavery in most British colonies
- 1834 Law took effect
- 800,000 slaves were freed
- £20m allocated to pay for “damages” suffered by owners
- 0 compensation for freed slaves
Source: Encyclopaedia Britannica

Records from the UK’s National Archives at Kew Gardens show how desperately the British struggled to end the internal trade in slaves for almost the entire duration of the colonial period.
They promoted legitimate trade, especially in palm produce. They introduced English currency to replace the cumbersome brass rods and cowries that merchants needed slaves to carry. They prosecuted offenders with prison sentences.
“By the 1930s, the colonial establishment had been worn down,” wrote Afigbo.
“As a result, they had come to place their hope for the extirpation of the trade on the corrosive effect over time of education and general civilisation.”

Working with the British
As a paramount chief, Nwaubani Ogogo collected taxes on behalf of the British and earned a commission for himself in the process.
He presided over cases in native courts. He supplied labourers for the construction of rail lines. He also willingly donated land for missionaries to build churches and schools.
My great-grandfather is renowned for his business prowess, strong leadership, immense contribution to society, and advancement of Christianity”

The house where I grew up and where my parents still live sits on a piece of land that has been in my family for over a century.
It was once the site of Nwaubani Ogogo’s guest house, where he hosted visiting British officials. They sent him envelopes containing snippets of their hair to let him know whenever they were due to arrive.
Nwaubani Ogogo died sometime in the early 20th Century. He left behind dozens of wives and children. No photographs exist of him but he was said to have been remarkably light-skinned.
In December 2017, a church in Okaiuga in Abia State of south-eastern Nigeria was celebrating its centenary and invited my family to receive a posthumous award on his behalf.
 Image copyrightADAOBI TRICIA NWAUBANI
Image copyrightADAOBI TRICIA NWAUBANITheir records showed that he had provided an armed escort for the first missionaries in the area.
My great-grandfather was renowned for his business prowess, outstanding boldness, strong leadership, vast influence, immense contributions to society, and advancement of Christianity.
The Igbo do not have a culture of erecting monuments to their heroes – otherwise one dedicated to him might have stood somewhere in the Umuahia region today.
“He was respected by everyone around,” my father said. “Even the white people respected him.”
–
Source: BBC



